Åsgard subsea compressors provide high availability
The world’s first subsea gas compression system has completed five years of service at the Åsgard gas field in the Norwegian Sea. It comprises two subsea HOFIM motor-compressor units from MAN Energy Solutions, which have run up 80,000 operational hours since September 2015 with an availability approaching 100%.
Randi Elisabeth Hugdahl, vice president of Åsgard Operations at Equinor, said: “Putting the compression system on the seabed near the wellheads improves recovery rates, and reduces capital and operating costs. Moreover, it has essential advantages in the form of improved safety for our employees and a significant reduction of the carbon footprint.”
She added that the HOFIM compressor systems had operated at full load since start-up, with overall performance exceeding expectations.
Equinor commissioned the equipment as pressure in Åsgard’s reservoirs would otherwise have been too low for stable flow. The two 11.5-MW motor-compressor units operate on the seafloor at a depth of 300 m (984 ft). According to MAN, the technology should extend the reservoirs’ productive life by a further 15 years, ensuring around 306 MMboe of production.
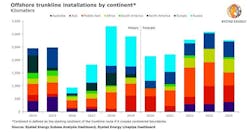
Middle East to lead offshore trunkline demand
The global oil and gas market demand for large-diameter offshore pipeline, known as trunkline, is set for an annual drop of 26% this year, with the total installations forecasted to reach 2,150 km (1,336 mi), according to Rystad Energy.
However, the consultant’s analysis suggests this downturn’s impact on trunkline demand is lighter than that of 2016, and recovery is likely to be swift, led by projects in the Middle East.
Although it is set for a significant drop from last year’s 2,913 km (1,810 mi), offshore trunkline demand is holding up much better now than during the previous downturn, when demand plummeted to just 938 km (583 mi) in 2016 from 2,488 km (1,546 mi) in 2015.
The consultant estimates the market’s recovery to be swift this time, as Middle Eastern projects are likely to propel demand to almost pre-COVID-19 levels already from 2022. From 2023, offshore trunkline installations are projected to exceed 3,000 km (1,864 mi).
Henning Bjørvik, energy service analyst at Rystad Energy, said: “The offshore trunkline market will recover to its prior levels in the next few years, driven by a handful of large transmission lines between regional markets and numerous export lines from upcoming offshore gas field developments.”
The global trunkline market is divided into upstream export lines connected to processing or production facilities, and transmission lines used for downstream transport between regions and markets. Although connected, the market drivers and characteristics of the two trunkline types are quite different.
Demand for export lines is directly related to offshore upstream development activity, where primarily gas field developments call for trunklines. Transport infrastructure accounts for a significantly larger portion of the value chain for gas developments than for oil, where operators can opt for export via buoy loading onto oil tankers. In project count terms, more than 90% of the nearly 100 offshore trunklines expected to be developed in the 2020-2024 period are gas export pipes.
Transmission line projects are more loosely connected to field developments. They normally originate in giant field development clusters that produce more gas than needed in local markets and can stretch out several hundred kilometers to reach import markets. According to the consultant, transmission line projects are often highly unpredictable due to geopolitics, and route decisions and legal approval stages are lengthy processes, especially for cross-country lines.
Transmission lines make up around half of the new trunklines forecasted up till 2024 measured by length, but in project count they amount to less than one-third. As a result, alterations in the timing of a few of these can throw the market around quite a bit.
Recent trunkline demand in Europe/Russia has been dominated by the contentious Nord Stream 2 dual transmission lines from Russia to Germany across the Baltic Sea, where installation started in 2018. Halted by existing US sanctions, 160 km (99 mi) of the 2,460-km (1,529-mi), 48-in. project remain to be laid. Rystad expects the project to be completed in 2021. North Sea oil and gas export lines have also contributed to demand.
Going forward, the EastMed transmission pipeline spanning the Mediterranean Sea from Israeli waters via Cyprus to mainland Greece is the largest driver in kilometer terms with offshore sections totaling 1,340 km (833 mi) expected to be installed between 2023 and 2026.
The Middle East trunkline market will continue to be dominated by export lines associated with giant offshore developments in Iran, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar. Asia/Pacific demand will be led by Australian export lines such as Barossa, Scarborough, and Browse LNG. African projects contributing to trunkline demand include Egypt’s Mediterranean Zohr field and the Mamba development in Area 4 off Mozambique, while the Americas is the only market expected to see a decline in installations in the coming years.
About the Author
Jessica Stump
Editor
Jessica Stump is editor of Offshore Magazine. She uploads and writes news to the website, assembles surveys and electronic newsletters, and writes and edits articles for the magazine. She was the summer editorial intern at Offshore in 2009 and 2010 before joining full time in April 2011. She has a journalism degree from Texas Tech University.