FIELD DEVELOPMENT: Facilities sharing, interconnection important in HP/HT developments
The start-up of production from the Elgin field in the UK North Sea occurred on Saturday March 31, 2001 by TotalFinaElf Exploration UK PLC. The initial pro duc tion rate of 13,500 b/d of condensate and 1.2 MMcm of gas, delivered by the Elgin field, is expected to increase over the coming months and to reach a plateau rate of 140,000 b/d of condensate (5.5% of UK production) and 13 MMcm of gas (4.5% of UK production). A combined total of 220,000 boe is expected when the Franklin field comes on stream in August.
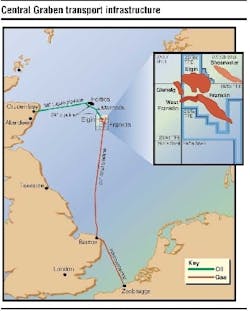
The combined Elgin/Franklin fields are the largest high pressure/high temperature (HP/HT) development in the world and its reserves will be produced from the deepest producing wells in the North Sea. The fields are located 240 km east of Aberdeen in the Central Graben Area of the North Sea's UK Sector.
At £1.65 billion, the Elgin/Franklin project is the most significant development on the UK Continental Shelf in recent years. Of the contracts awarded for the Elgin/Franklin project, 82% were placed with UK industry. Completed within budget and within 48 months from sanction to start-up, the Elgin/Franklin project employed more than 5,000 people during peak construction and created 160,000 man-months of work in the UK.
Michel Contie, Managing Director, TotalFinaElf Exploration UK PLC said: "These HP/HT fields posed numerous technical challenges throughout their development and what we have achieved is a significant step forward in the use of highly innovative technology for the oil industry. This new development will bring a new dimension in the UK with 400,000 boe/d of operated production. Our company, our partners, contractors, and government authorities have taken a shared approach to safety, innovation, best practices, and cooperation, the results of which we can be proud of today."
The proximity of the Elgin and Franklin fields made it possible to develop them in tandem. Each field has its own wellhead platform with production from both fields being processed through one central facility. A production/utilities/ quarters platform is (PUQ) located in the Elgin field. TotalFinaElf Exploration UK PLC is the operator with the following participants: E.F.Oil and Gas Limited (46.173%), Agip (U.K.) Lim i ted (13.867%), BG International Limited (12.350%), Agip Elgin/Franklin Limited (8.000%), Ruhrgas UK Exploration and Production Limited (5.200%), Esso Exploration and Production UK Limited (4.375%), Texaco Britain Limited (3.900%), Dyas UK Limited (2.1875%), ONEPM (UK) Limited (2.1875%), and ARCO British Ltd (1.760%). E.F. Oil and Gas Limited is a company in which the shares are held 77.5% by Elf Exploration UK PLC and 22.5% by Gaz de France.
Field geology
The Elgin and Franklin fields, which contain HP/HT gas condensate of around 1,100 bar and 200° C, lie in a structurally complex area in the southern part of Central Graben over 5km below the seabed. The Elgin field comprises a complex faulted anticlinal structure and the Franklin field a tilted fault block.
The principal reservoir comprises highly bioturbated, very fine grained, shallow marine sandstones of the Upper Jurassic Fulmar Formation, locally named the Franklin Sand. Hydrocarbons have also been encountered in the Pentland Formation of Middle Jurassic age. The good reservoir quality is due to a significant amount of secondary porosity, which has been preserved by the extreme overpressure. The Elgin field is located in Blocks 22/30b, 22/30c and 29/5b. Elgin was discovered in 1991 by well 22/30c-8 and appraised by wells 22/30c-10 and 22/30c-13, all of which were drilled from a single wellsite.
Recoverable reserves are estimated to be 25.914 bcm of gas, 3.598 million tons of NGL, and 31.331 million tons of condensate, with recovery factors of 63% for gas and 59% for condensate from seven producing wells. The API gravity of the condensate is 0.806 degrees, with a sulfur content of less than 0.01%. Peak production is estimated to be 14.6 MMcm/d of gas and 175,000 b/d of liquids. The 12 slot-4 leg-steel jacketed wellhead platform was installed in a water depth of 93 meters. Total weight of the platform including piles was 6,083 tons with a deck dimension of 25.5 meters by 34 meters. Wells were drilled through the dedicated slots by a cantilever type jackup rig.
Franklin field
The Franklin field is located 6.5 km southeast of Elgin and lies within Block 29/5b. Franklin was discovered by Ultramar in 1986 by well 29/5b-4, operated by Ranger in the framework of a farm-in obligation and appraised by wells 29/5b-6 and 29/5b-8 all of which have been plugged and abandoned.
Recoverable reserves are estimated to be 25.635 bcm of gas, 2.241 million tons of NGL, and 18.253 million tons of condensate, with recovery factors of 47% for gas and 46% for condensate from six producing wells. The API gravity of the condensate is 0.806 degrees with a sulfur content of less than 0.01%. Peak production is estimated to be 6.7 MMcm and 41,000 b/d of liquids. The 9 slot-4 leg-steel jacketed wellhead platform was installed in a water depth of 93 meters. Total weight of the platform including piles was 6,283 tons with a deck dimension of 25.5 meters by 46 meters. Wells were drilled through the dedicated slots by a cantilever type jackup rig.
Field installations
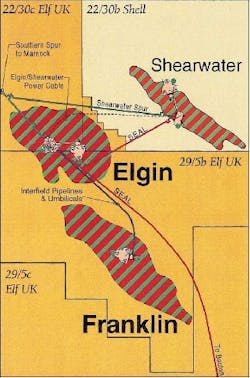
The Elgin and Franklin fields each have their own dedicated wellhead platform that are connected to the PUQ platform. Hydrocarbons from both fields will be processed on the PUQ and then carried ashore via separate export lines. The Elgin wellhead platform is connected to the PUQ by a bridge along which its hydrocarbons will be piped and the Franklin platform by an interfield pipeline system.
The jackup PUQ platform comprises central process facilities for both fields. The main advantage of the jackup PUQ platform is that it could be built onshore as one complete unit alleviating the need for heavy lifts offshore and that it will be refloated and totally removed from site once the fields have been depleted.
The PUQ is similar to a traditional jackup drilling rig except that it has no drilling facilities on board. Inside the triangular shaped hull are the utilities (the main power distribution system, compressed air system, and workshops) and the living quarters (69 beds, dining room, galley, recreation rooms, and main control room). The main deck of the hull supports the topside facilities and contains the production equipment (power generation and process support systems).
Hydrocarbon export
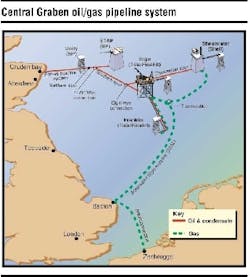
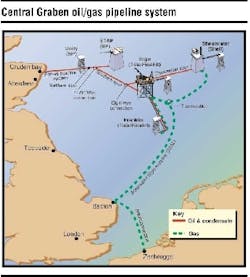
Hydrocarbons produced from Elgin and Franklin wells will be collected, separated, and treated at the central processing facility on the PUQ. Liquid hydrocarbons will be exported through the BP-operated Forties Pipeline System via Cruden Bay to Kinneil for processing. To transport the liquid hydrocarbons via the Forties Pipeline System, a new 24-in. diameter spurline, the Southern Spur, has been laid from the PUQ to a subsea connection (a Wye piece) close to BP's Marnock platform. Liquid hydrocarbons from the nearby Shell-operated Shearwater platform will also be transported through this spurline via the Shearwater Spur, tied in at a Wye piece about 2 km north of the PUQ.
Elf Exploration was operator during the design and pre-commissioning phases of the Southern and Shearwater Spur with BP becoming operator for commissioning and production start-up. In order to export the commercial quality gas from Elgin/Franklin and Shearwater, a new 34-in. diameter, 468-km pipeline from the developments to Bacton was installed. The SEAL (Shearwater Elgin Area Line) pipeline originates at Shearwater with Elgin/Franklin tied in via a subsea T connection. A new gas reception facility at Bacton delivers SEAL gas to the Transco terminal for the UK market and to the Interconnector pipeline for transmission to the Continent. Elf Exploration was operator during the design and pre-commissioning phases of the SEAL pipeline with Shell becoming operator for the commissioning and production phases.
The commonality in the development schemes of Elgin/Franklin and Shearwater fields has led to the sharing of the gas and liquid hydrocarbon export arrangements and an interlinking power cable between the PUQs, allowing efficiencies in power supplies between the two facilities.